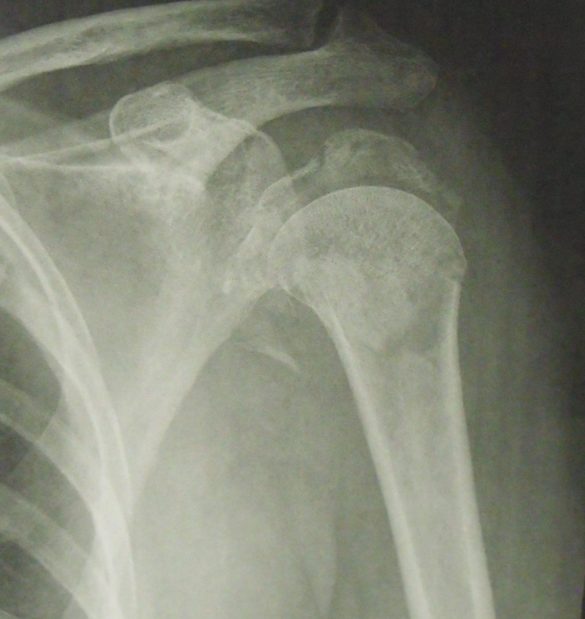
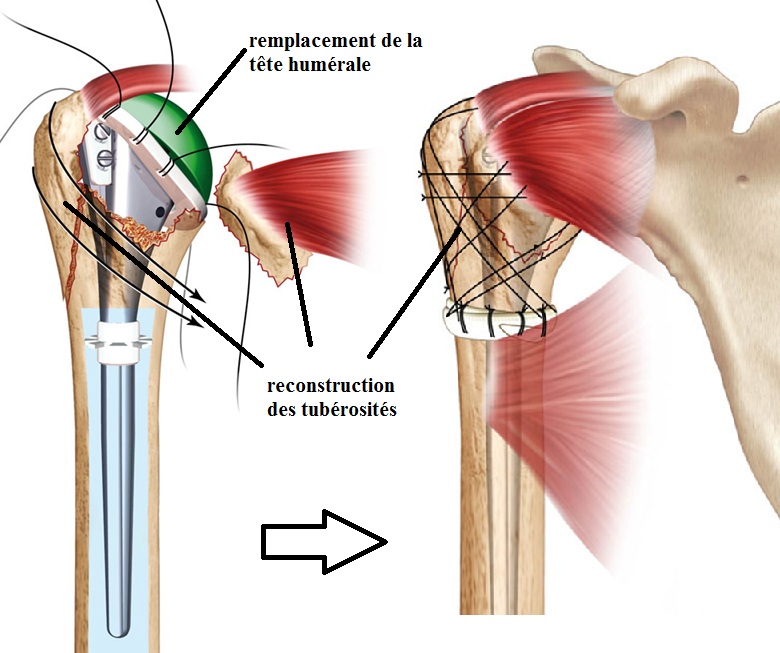
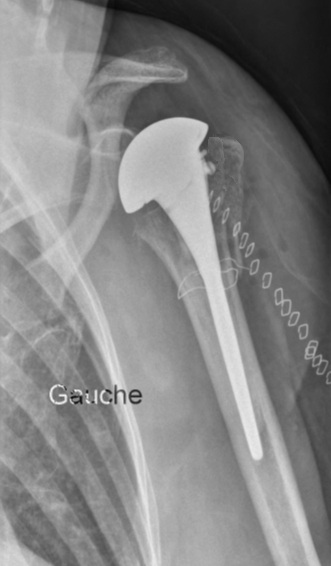
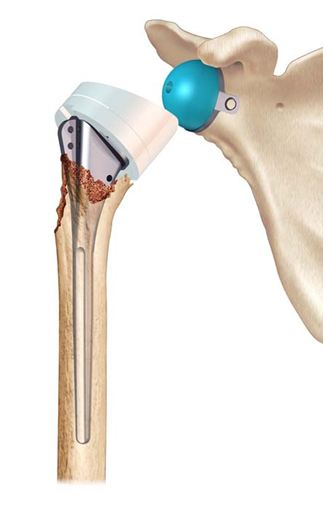
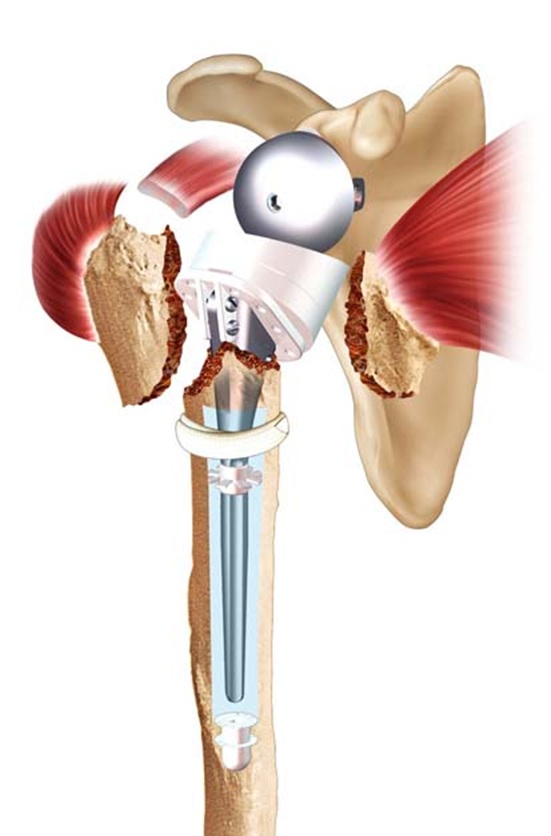
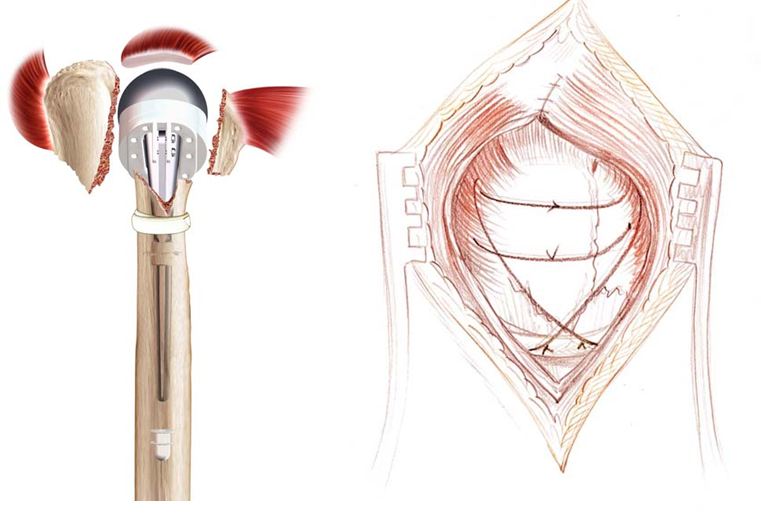
In addition to conservative orthopedic treatment (from a fracture with little or no displacement to 4 fragments) and osteosynthesis, a shoulder prosthesis for fracture can be decided.
The principle is then to replace the humeral head with a portion of metal sphere, in elderly patients or in case of supposed major risk of necrosis of the humeral head.
Like prostheses for osteoarthritis (see dedicated chapter) there are several possibilities and assemblies: